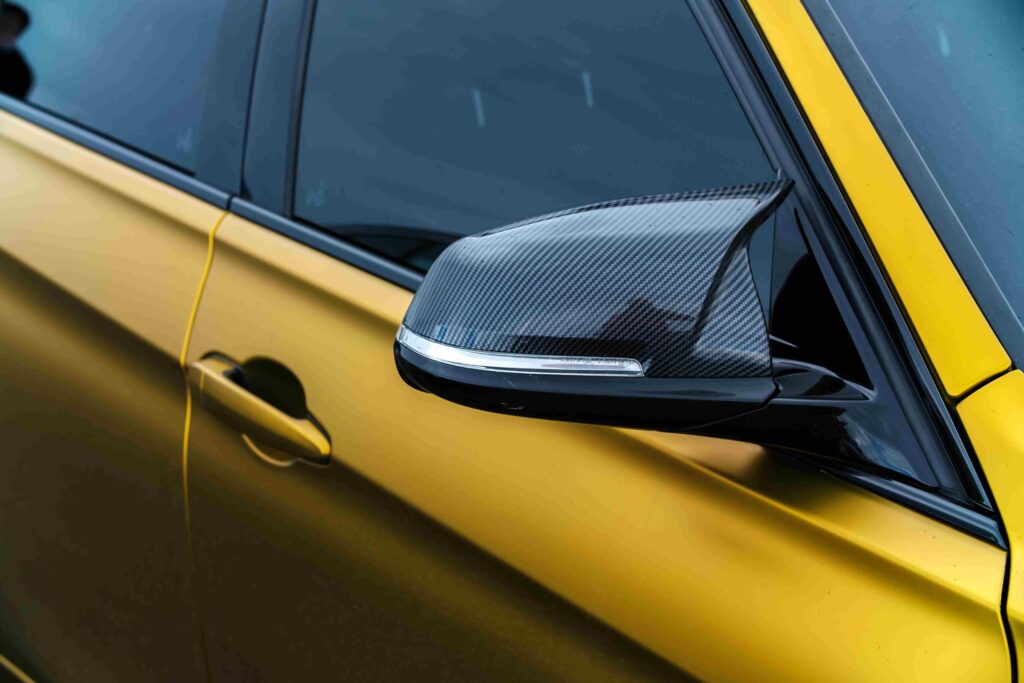
Carbon Fiber VS. Fiberglass Body Panels
Making the decision between carbon fiber vs. fiberglass body panels can be difficult when you aren’t informed. When it comes to choosing between carbon fiber and fiberglass for your vehicle’s body panels, it’s crucial to comprehend the fundamental disparities between these two materials. Despite their interchangeable use in various applications, carbon fiber and fiberglass have unique attributes that make them suitable for specific purposes.
When considering enhancements to your vehicle, such as incorporating carbon fiber or fiberglass components, it’s equally crucial to safeguard your investment with a reliable warranty. The Mopar Extended Warranty covers potential repairs or replacements of essential components, thus complementing the high-performance and aesthetic benefits brought by materials like carbon fiber.
Strength
In the realm of structural strength, both carbon fiber and fiberglass outperform steel, marking a significant advancement in material capabilities. However, when scrutinizing their specific strengths, it becomes evident that industrial-grade carbon fiber emerges as the frontrunner, exhibiting a remarkable superiority of over 20 percent compared to the highest-quality fiberglass available.
What sets carbon fiber apart is its extraordinary strength-to-weight ratio, a metric that stands as a testament to its unparalleled robustness. In practical terms, carbon fiber showcases a ratio approximately twice as potent as that of fiberglass. This exceptional characteristic, positions carbon fiber as the preferred choice for applications where strength is not merely desired but paramount. Whether in the aerospace industry, automotive engineering, or other high-performance domains, the inherent strength of carbon fiber proves to be a decisive factor, offering an optimal combination of durability and weight efficiency.
Stiffness and Flexibility
Carbon fiber stands out for its exceptional stiffness, rendering it particularly well-suited for applications demanding a high degree of rigidity, especially in mechanical components. The tensile modulus of carbon fiber surpasses that of fiberglass by a factor of four, underscoring its superior structural integrity and strength.
Conversely, fiberglass, characterized by its innate flexibility, becomes the material of choice in scenarios where adaptability and suppleness take precedence over rigid structural requirements. This flexibility makes fiberglass an optimal selection for applications where the emphasis is not on maintaining a fixed form but rather on accommodating dynamic conditions or absorbing impacts without compromising the overall integrity of the structure. The versatility of fiberglass, stemming from its pliable nature, allows it to excel in situations where the need for malleability overrides the necessity for unyielding rigidity. This nuanced balance between rigidity and flexibility positions carbon fiber and fiberglass as versatile materials, each uniquely tailored to meet the specific demands of diverse applications within various industries.
Weight
Both carbon fiber and fiberglass stand out for their exceptional lightweight properties, presenting a notable departure from traditional metals such as steel and aluminum. However, delving deeper into the specifics, carbon fiber tends to exhibit a weight advantage of approximately 15% over fiberglass composites. This nuanced difference becomes particularly critical in specialized fields like aerospace and car racing, where the imperative to minimize weight significantly influences performance outcomes. The ability of carbon fiber to provide enhanced strength with reduced weight makes it a preferred choice in these demanding applications, contributing to superior aerodynamics and overall efficiency in high-performance scenarios. This underscores the nuanced considerations and advantages that come into play when evaluating these materials for specific industries and performance-driven contexts.

Thermal Expansion Dynamics
Unlike most materials, carbon fiber expands in cold temperatures due to its negative coefficient of thermal expansion. The interplay with its matrix, which contributes a positive coefficient, often results in a close-to-neutral overall coefficient of thermal expansion. In extreme temperature conditions, carbon fiber may outperform fiberglass, showcasing its resilience in cold environments. This unique thermal behavior adds to carbon fiber’s versatility, making it an appealing choice for applications where temperature fluctuations are a critical consideration.
Corrosion Resistance
Both carbon fiber and fiberglass showcase remarkable resistance to corrosion, positioning them as excellent choices for applications subjected to potentially corrosive elements such as harmful chemicals, corrosive acids, or abrasive environments. Their inherent ability to withstand these harsh conditions not only ensures the longevity of the materials but also enhances their suitability for a wide array of industrial and practical settings where durability in challenging environments is a critical factor. This corrosion resistance feature makes both materials highly sought-after options, providing reliability and longevity even in the face of adverse external factors.
Cost Considerations
When evaluating the economic aspects of fiberglass and carbon fiber components, it’s essential to delve into the intricacies of their cost structures. Fiberglass, renowned for its widespread applications, enjoys a reputation for being more cost-effective. This economic advantage primarily stems from its versatility, as fiberglass finds applications in various industries, leading to economies of scale and subsequently lower manufacturing costs.
On the flip side, the production of carbon fiber involves a notably intricate process. The manufacturing of carbon fiber-reinforced polymer requires precision and specialized techniques, contributing to a higher price tag. The meticulous crafting of carbon fiber, with its actual carbon fibers woven into a polymer fabric, demands advanced technology and expertise, further elevating the production costs. Therefore, the higher investment associated with carbon fiber components reflects the intricate manufacturing processes that contribute to its superior strength and lightweight characteristics. In essence, the cost dichotomy between fiberglass and carbon fiber is a nuanced interplay of versatility, scale, and manufacturing intricacies that discerning consumers should consider when making informed choices for their specific applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Body Kit
If you’re considering modifying your car with a body kit, the choice between fiberglass and carbon fiber becomes crucial. Let’s delve into the characteristics of each material to help you make an informed decision.
Fiberglass
Fiberglass components emerge as a practical choice for various applications due to their ease of production and cost-effectiveness. Their lightweight nature makes them highly desirable, offering advantages in terms of fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Moreover, fiberglass exhibits resilience to temperature changes, ensuring durability in diverse environmental conditions. The material’s compatibility with paint is noteworthy, allowing for seamless customization and a visually appealing finish.
However, it is essential to acknowledge the inherent rigidity of fiberglass, which introduces a level of complexity during the installation process. The stiffness of the material, while providing structural integrity, requires meticulous handling to ensure a precise fit. Moreover, this rigidity raises concerns about the vulnerability of the finished product to potential shattering, particularly in situations involving impact or stress.
In navigating the realm of Fiberglass components, the significance of quality cannot be overstated. Opting for reputable manufacturers becomes paramount in ensuring not only the structural integrity of the finished product but also a superior fit and finish. A commitment to excellence from manufacturers contributes significantly to the overall reliability and longevity of fiberglass parts, making informed choices in selecting reputable sources a critical aspect of any automotive customization endeavor.
Carbon Fiber
Carbon Fiber, a composite material comprising a polymer matrix reinforced with actual carbon fibers, offers unparalleled strength and a sleek appearance, making it ideal for racing and high-performance applications. Despite higher production costs, the aesthetic appeal and performance benefits justify the investment. Beyond structural strength, carbon fiber’s unique weave pattern and glossy finish add sophistication to a vehicle’s design. The lightweight nature of carbon fiber contributes to improved fuel efficiency, agility, and overall performance, making it a compelling choice for enthusiasts and professionals seeking excellence on the road and the track.
In the end, both fiberglass and carbon fiber excel in providing superior strength-to-weight ratios for various applications. However, the choice depends on your specific needs and preferences. Whether you opt for the affordability of fiberglass or the high-performance allure of carbon fiber, selecting the right material and installation expertise will ensure a stunning and unique final result for your vehicle.